Study Finds Historic Drop in National Reading and Math Scores Since Adoption of Common Core Curriculum Standards
Read coverage of this report in Patch, Breitbart, The Washington Examiner, and San Antonio Express News.
Lower performing students hardest hit
BOSTON – As we approach the 40th anniversary of the establishment of the United States Department of Education in May, shocking trends in student performance should lead us to reconsider the federal role in education and whether the initiative for policymaking should be returned to local schools, communities, and states.
Breaking with decades of slow improvement, U.S. reading and math scores on the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) and other assessments have seen historic declines since most states implemented national Common Core English and math curriculum standards six years ago, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute.
While Common Core was promoted as improving the international competitiveness of U.S. students in math, our international standing has remained low while the skills of average and lower performing American students have dropped in both math and reading.
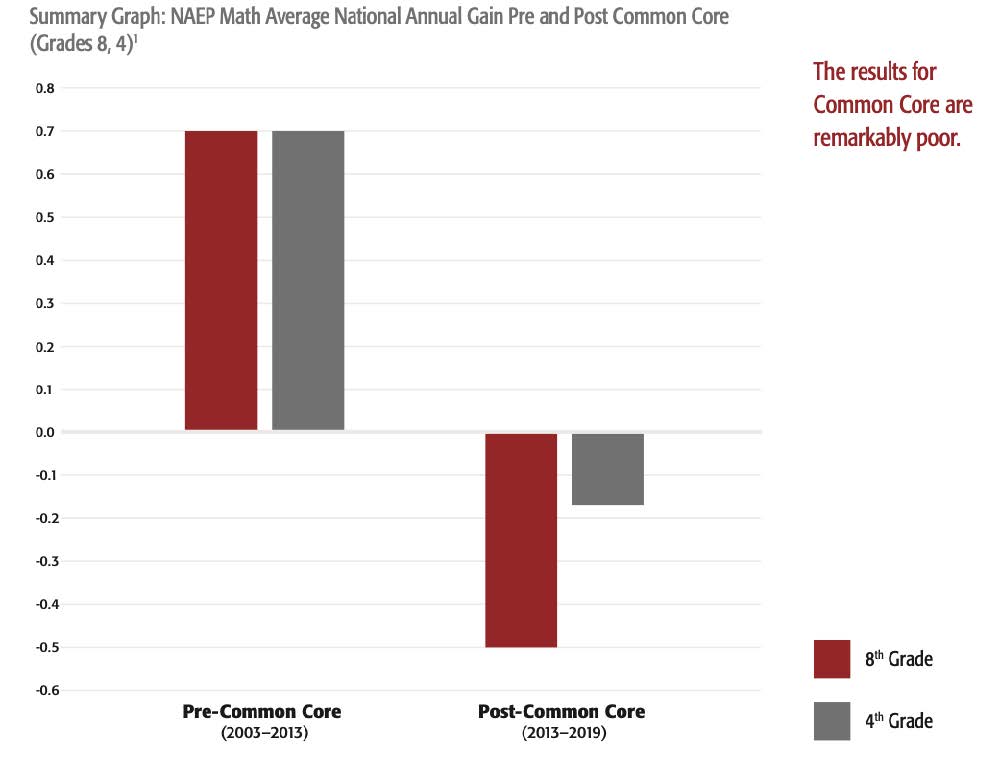
Nationally, fourth- and eighth-grade NAEP math scores were rising gradually in the years before Common Core was implemented (2003-2013). Post-Common Core, scores at both grades have fallen, eighth grade at nearly the same rate as it was previously increasing.
The declines are most acute for the lowest-achieving students, increasing inequality. Scores for students at the 90th percentile have mostly continued their pre-Common Core trend of gradual improvement. But the farther behind students were, the more substantial the declines, with the biggest drops occurring for those at the 25th and 10th percentiles.
“The sustained decline we’re now seeing, especially among our most vulnerable students, simply cannot be allowed to continue,” said Theodor Rebarber, author of “The Common Core Debacle.”
U.S. students fare better in reading than they do in math when compared to international competitors, but U.S. reading trends are similar to those seen in math, with gradual pre-Common Core improvement replaced by declines after Common Core was implemented.
From 2003 to 2013, national fourth- and eighth-grade reading scores were increasing at an average of about half of a point each year. Since 2013, fourth-grade reading scores have been falling by less than half of a point each year, while eighth-grade scores have dropped by nearly a full point a year.
Rebarber also finds that Common Core is a product of the misguided progressive pedagogies and biases of the education establishment that developed it. “Several of us allied with Pioneer Institute have been pointing out, ever since it was introduced, the deeply flawed educational assumptions that permeate the Common Core and the many ways in which it is at odds with curriculum standards in top-achieving countries.” Unfortunately, the disappointing results of Common Core—particularly for lower performing students—were predicted in 2010.
“Nearly a decade after states adopted Common Core, the empirical evidence makes it clear that these national standards have yielded underwhelming results for students,” said Pioneer Executive Director Jim Stergios. “The proponents of this expensive, legally questionable policy initiative have much to answer for.”
“It’s time for federal law to change to allow states as well as local school districts to try a broader range of approaches to reform,” added Rebarber. “With a more bottom-up approach, more school systems will have the opportunity to choose curricula consistent with our international competitors and many decades of research on effective classroom teaching.”
State Analyses (See Appendix)
The study also includes summary analyses of pre- and post-Common Core performance in seven states: Massachusetts, California, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Kentucky, and New York. These states, chosen mainly based on their size and geographic distribution, generally reveal a pattern similar to the national results.
About the Author
Theodor Rebarber has worked on education reform and policy for three decades in the public, nonprofit and private sectors. He currently leads nonprofit AccountabilityWorks, which conducts education policy research and offers online testing services at AWSchoolTest.com. Previously, he was co-founder and chief education officer of a venture capital-backed charter school management company. Rebarber served as a senior staff member in Congress. He worked on education policy, including curriculum standards and testing, at the U.S. Education Department for the office of research and at the Vanderbilt Institute for Public Policy Studies. He has testified before Congress and state legislatures as well as developed analyses on a range of education policy topics.
About Pioneer
Pioneer Institute is an independent, non-partisan, privately funded research organization that seeks to improve the quality of life in Massachusetts through civic discourse and intellectually rigorous, data-driven public policy solutions based on free market principles, individual liberty and responsibility, and the ideal of effective, limited and accountable government.
Get Updates on Our Education Research
Massachusetts
In Massachusetts, from 2003 to 2013, before implementation of Common Core, NAEP fourth- and eighth-grade math scores were rising. Massachusetts had the highest rate of improvement among the states analyzed prior to Common Core. Post-Common Core, they’ve declined at nearly the same rate as they were previously improving.


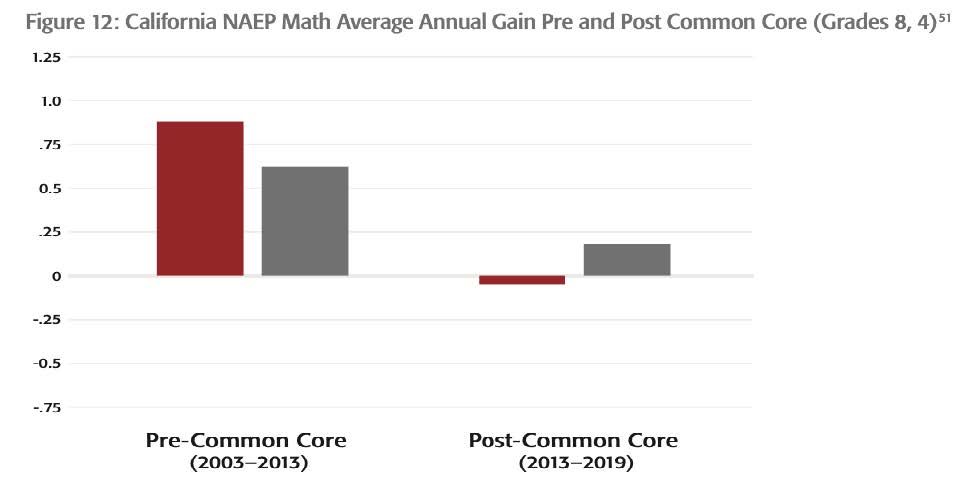
California
In California, pre-Common Core NAEP fourth- and eighth-grade math scores were rising. Post- Common Core, fourth-grade math scores have barely risen by less than 0.2 points a year and eighth-grade scores have dropped.
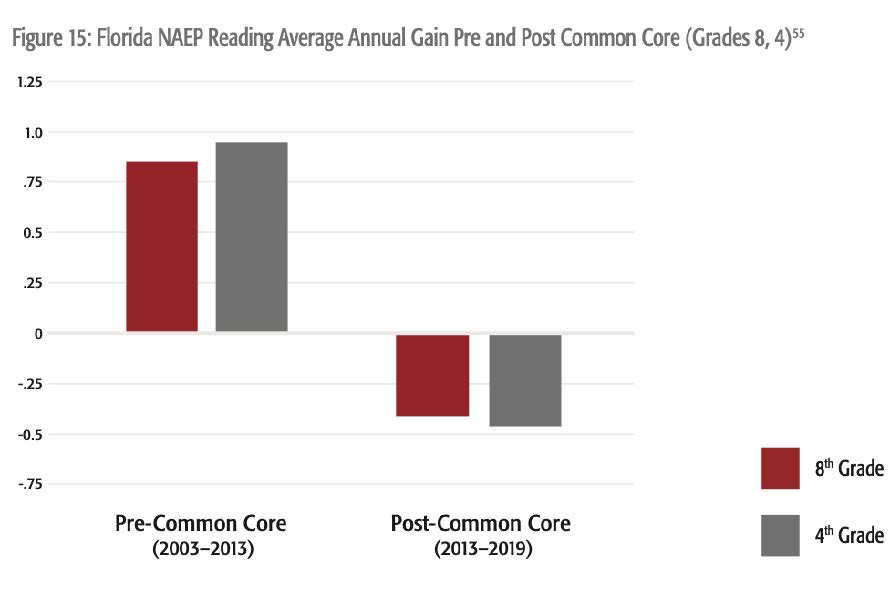
Florida
In Florida, Pre-Common Core NAEP fourth- and eighth-grade reading scores were rising. Post-Common Core scores have fallen.
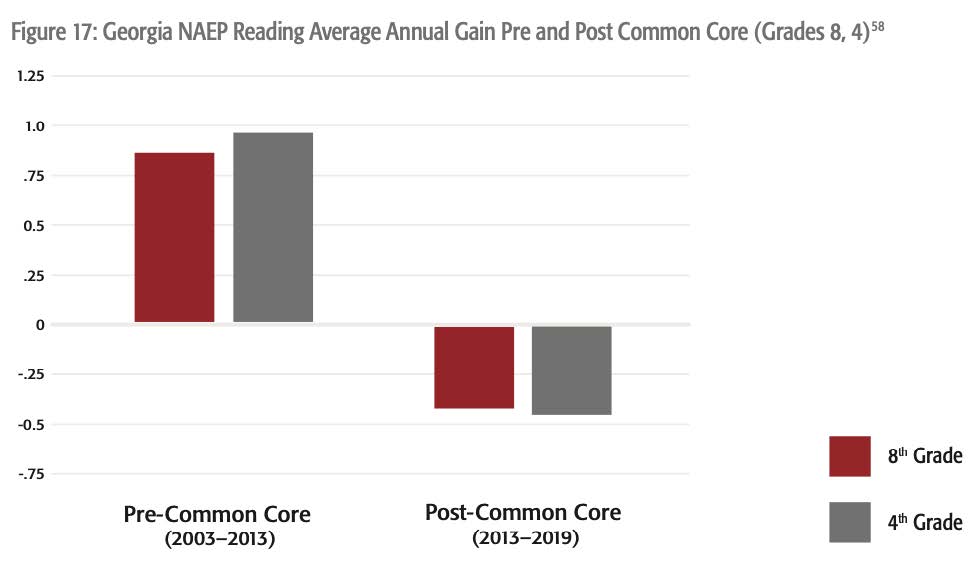
Georgia
In Georgia, pre-Common Core, NAEP fourth- and eighth-grade reading scores were rising. Post-Common Core, they’ve fallen.
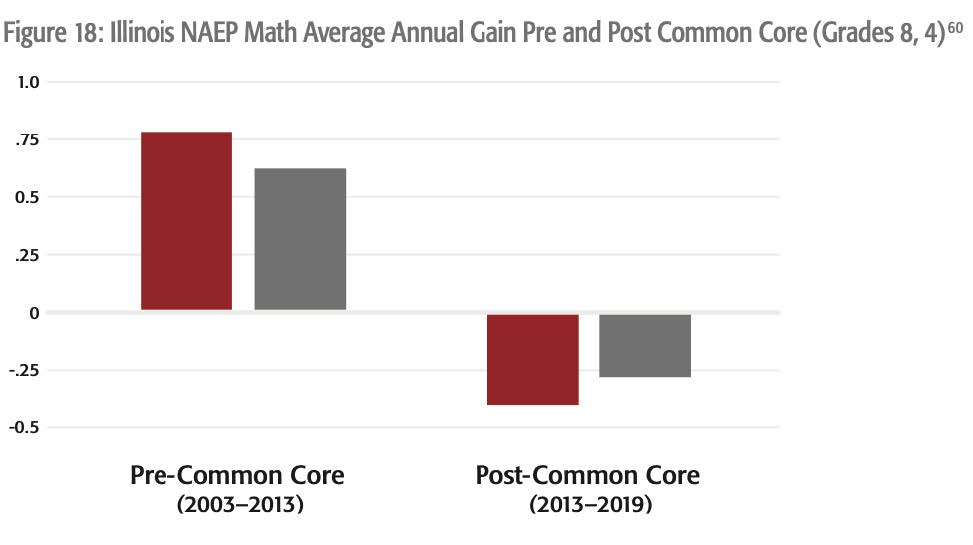
Illinois
In Illinois, before Common Core, NAEP fourth- and eighth-grade math scores were rising. Post-Common Core, they’ve fallen.
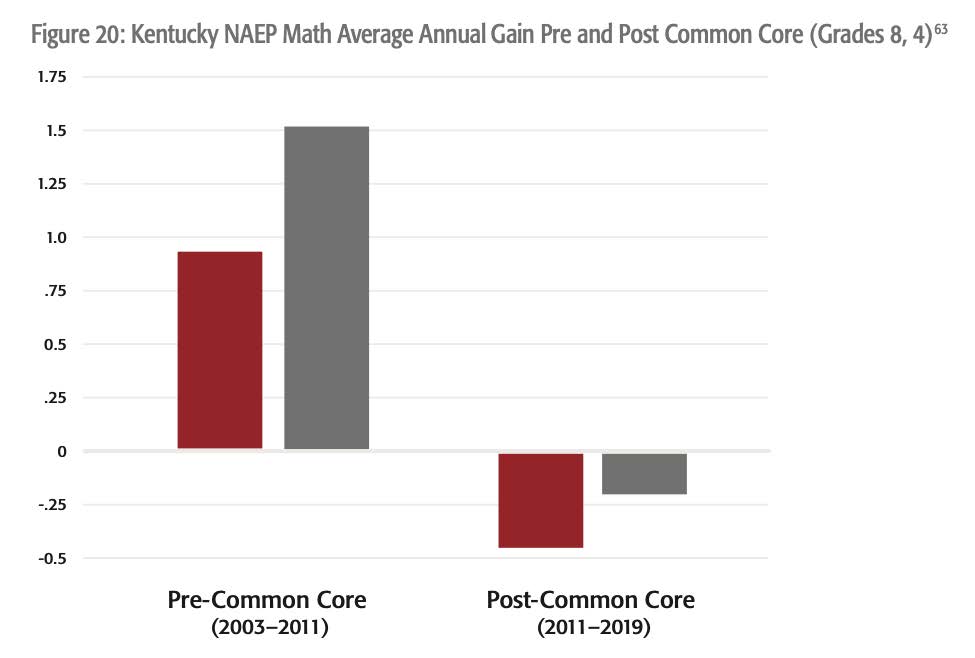
Kentucky
Kentucky was the first state to adopt and implement Common Core. In the years prior to imple-mentation (in this case, 2003-2011), fourth-grade math scores were rising at a substantial pace. Post-Common Core (2011-2019), fourth- and eighth-grade scores have fallen.
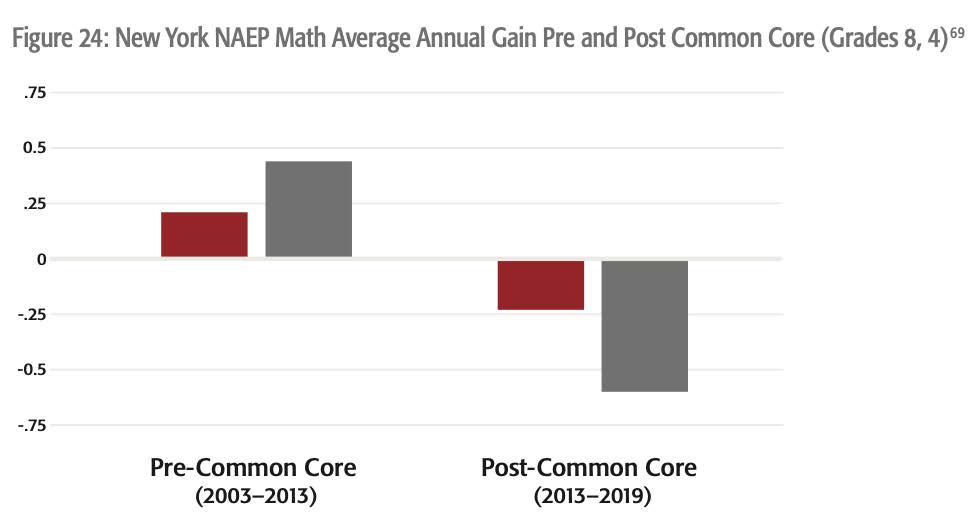
New York
New York implemented Common Core in 2013. Prior to Common Core, NAEP fourth-grade math scores were rising. Post-Common Core, fourth- and eighth-grade scores have fallen, espe-cially in mathematics.