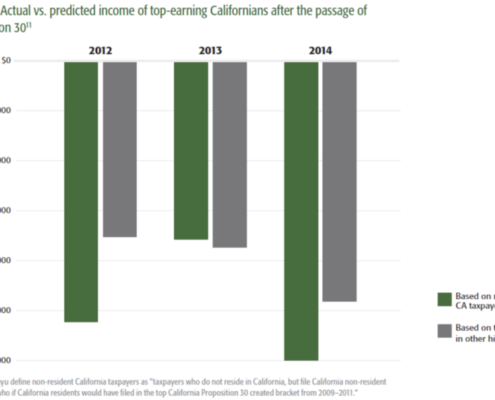
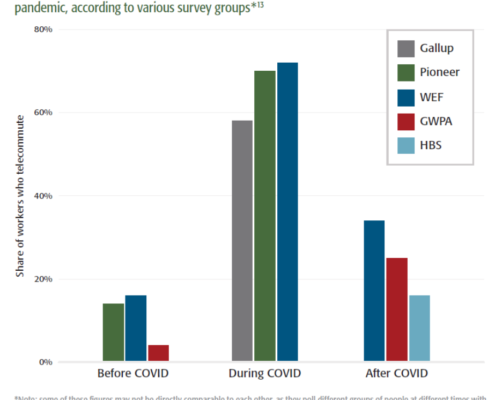
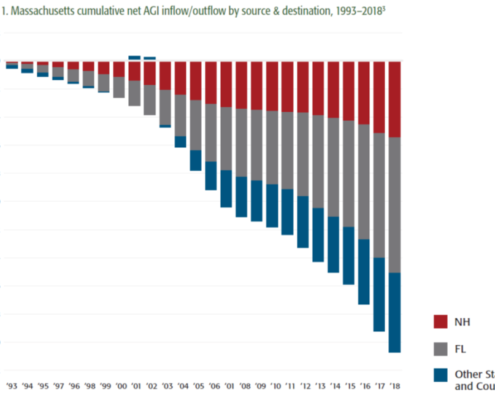
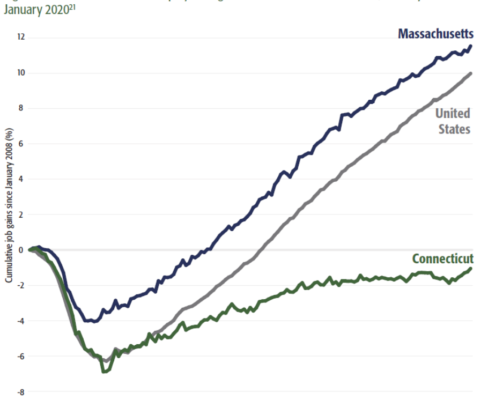
Study Finds SALT Deduction Cap, Graduated Income Tax Will Combine to More Than Double Tax Burden on Some Households
BOSTON – A provision of the federal Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 strictly limiting deductions for state and local taxes (SALT) will greatly exacerbate the adverse effects of a proposal to create a constitutionally mandated graduated income tax, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute.
Before tax year 2018, Americans who itemized deductions were able to write off the full value of the state and local taxes they paid from their federal tax return. Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, however, only the first $10,000 paid in state and local taxes are eligible for deduction, which resulted in a year-over-year 80 percent decrease in the total amount of SALT deductions claimed.
“The 2017 federal curb on SALT deductions has already exposed small businesses and retirees to the full force of state tax policies in blue states like Massachusetts,” said Greg Sullivan, who co-authored The SALT Cap: An Accelerator for Tax Flight from Massachusetts with Andrew Mikula and Liv Leone. “The proposed tax would double down on small businesses and retirees, with the effect of lessening business investment, lowering home values, and producing fewer jobs.”
The Massachusetts Department of Revenue estimated that the average Massachusetts taxpayer subject to the surtax in 2019 would see a 58.2 percent increase in state income taxes. But when the SALT deduction cap is factored in, Massachusetts taxpayers with incomes of $1 million or more will see an increase of 147.5 percent in their average state income tax payment net of the federal tax deduction benefit, from $101,295 to $250,655, because of the combined effect of the SALT cap and the surtax.
While Congress has debated repealing the SALT deduction cap in recent weeks, doing so will likely agitate both progressives, who argue that the SALT deduction largely benefits the wealthy, and conservatives, who question why the federal government should bail out people who choose to live in high-tax states and cities.
While Massachusetts has passed legislation to offset the impact of the SALT limitation at the federal tax level, this workaround does not change the amount of taxable income a pass-through entity is responsible to report to its members as their proportionate share of taxable income at the state level. Thus the workaround tax credit is not relevant to the impact of the proposed graduated income tax amendment in Massachusetts.
When New York passed a millionaires’ tax in April that is similar to the Massachusetts surtax proposal, seasoned economist Larry Summers warned that, without a repeal of the SALT deduction limitation, the legislation could send the Empire State into “a downward spiral.” This likely alludes to the economic impact of the tax base erosion, revenue volatility, and disinvestment associated with such tax increases.
“Massachusetts lawmakers either did not understand the many ways in which the graduated income tax amendment will harm our competitiveness or they chose, because of political expediency, to ignore those impacts,” said Pioneer Institute Executive Director Jim Stergios. “The SALT cap and other limits on itemized deductions will make the graduated income tax an albatross around the neck of the Bay State’s job creators and investors.”
About the Authors
Gregory Sullivan is Pioneer’s Research Director. Prior to joining Pioneer, Sullivan served two five-year terms as Inspector General of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts and was a 17-year member of the Massachusetts House of Representatives. Greg holds degrees from Harvard College, The Kennedy School of Public Administration, and the Sloan School at MIT.
Andrew Mikula is a former Economic Research Analyst at Pioneer Institute and current candidate for a Master’s in Urban Planning at Harvard University.
Liv Leone is a Research Associate at Pioneer Institute. Liv holds a bachelor’s and a master’s degree in political science from Boston University. Joining Pioneer in 2021, she conducts research with data from MassEconomix, and supports Pioneer’s fields of research, including taxation and regulation.
Pioneer’s mission is to develop and communicate dynamic ideas that advance prosperity and a vibrant civic life in Massachusetts and beyond. Pioneer’s vision of success is a state and nation where our people can prosper and our society thrive because we enjoy world-class options in education, healthcare, transportation and economic opportunity, and where our government is limited, accountable and transparent. Pioneer values an America where our citizenry is well-educated and willing to test our beliefs based on facts and the free exchange of ideas, and committed to liberty, personal responsibility, and free enterprise.
Get Updates on Our Economic Opportunity Research
Related Posts: