Study Finds Deep Flaws in Advocates’ Claims that the Massachusetts Tax Code is Regressive
Even using ITEP’s biased analyses, Massachusetts is more progressive than most states
BOSTON – Proponents of a state constitutional amendment to add a 4 percent surtax on all households with annual income above $1 million frequently cite 2015 data from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, which argues that the Massachusetts tax code is regressive, but a new study published by Pioneer Institute debunks many of the underlying assumptions used in ITEP’s 2015 report.
Among other flaws, the ITEP analysis excludes some of the most progressive elements of the tax code, uses outdated data, and even includes some regressive elements of the federal tax code in a state-level analysis. ITEP also makes broad and dubious assumptions that taxes levied on corporations and landlords are passed on to consumers, tenants, and workers.
Surtax proponents also ignore that ITEP’s most recent tax incidence analysis ranks Massachusetts as having a more progressive state tax code than 29 other states. Massachusetts’ Tax Inequality Index score was -3.10 in 2018, better than the -3.48 average score of the other 49 states and D.C.
“Even ITEP says that, compared to other states, Massachusetts has a relatively progressive tax code,” said Greg Sullivan, who co-authored Are Massachusetts taxes regressive? A common argument for a graduated income tax relies on a deeply flawed and outdated study with Andrew Mikula. “But ITEP’s analysis still relies on some faulty assumptions about who ultimately bears the burden of corporate and property taxes, which make the tax code seem artificially onerous for the poor.”
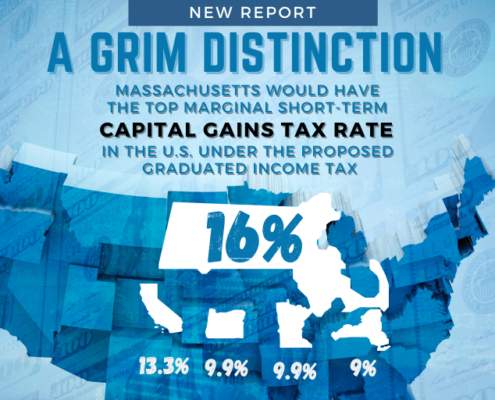
The new Pioneer study also emphasizes how Massachusetts gets a vastly disproportionate share of income tax revenue from the wealthy. The top 10 percent of Massachusetts taxpayers paid 38.2 percent more than the bottom 90 percent in 2017, and that figure would rise to 68.1 percent more if the surtax passes. The richest 0.5 percent of taxpayers currently pay 24 percent of state income taxes in the Commonwealth, and this would rise to 32.5 percent if the surtax is passed. This is significant because a heavy reliance on the wealthy to fill state coffers has been linked to high revenue volatility and other budget problems.
“An over-reliance on wealthy taxpayers, especially when cyclical revenue streams like capital gains taxes are factored in, can create significant risk for state budget writers during the next recession,” said Pioneer Institute Executive Director Jim Stergios. “Add to that the current trend, whereby Massachusetts is losing almost a billion dollars of wealth a year because of relocations to low- and no-tax states. Then factor in easier job mobility post-pandemic. The sum total is that tax increases are a risky move right now.”
Other think tanks have criticized ITEP’s work, including the Tax Foundation, which in 2018 accused ITEP of “cherry-picking” in order to “make every state’s tax code look significantly more regressive” than it actually is.
Pioneer reached out to ITEP to clarify certain aspects of their methodology, but they have failed to respond as of this writing.
About the Authors
Andrew Mikula is Economic Research Analyst at Pioneer Institute. Mr. Mikula was previously a Lovett & Ruth Peters Economic Opportunity Fellow at Pioneer Institute and studied economics at Bates College.
Gregory Sullivan is Pioneer’s Research Director. Prior to joining Pioneer, Sullivan served two five-year terms as Inspector General of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts and was a 17-year member of the Massachusetts House of Representatives. Greg is a Certified Fraud Investigator, and holds degrees from Harvard College, The Kennedy School of Public Administration, and the Sloan School at MIT.
Pioneer’s mission is to develop and communicate dynamic ideas that advance prosperity and a vibrant civic life in Massachusetts and beyond. Pioneer’s vision of success is a state and nation where our people can prosper and our society thrive because we enjoy world-class options in education, healthcare, transportation and economic opportunity, and where our government is limited, accountable and transparent. Pioneer values an America where our citizenry is well-educated and willing to test our beliefs based on facts and the free exchange of ideas, and committed to liberty, personal responsibility, and free enterprise.
Get Updates on Our Economic Opportunity Research
Related Content