New Study Highlights Economic Fallout from California’s 2012 Tax Hike
BOSTON – A 2012 income and sales tax increase in California, named “Proposition 30,” stifled business activity, accelerated out-migration among the wealthy, and ultimately reduced the state’s tax base, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute that aims to share empirical data about the impact of tax policy decisions.
“The academic literature on Proposition 30 is among the strongest evidence we have that behavioral responses to tax hikes occur disproportionately among the wealthy,” said Andrew Mikula, author of “How a 2012 income tax hike cost California billions of dollars in economic activity.”
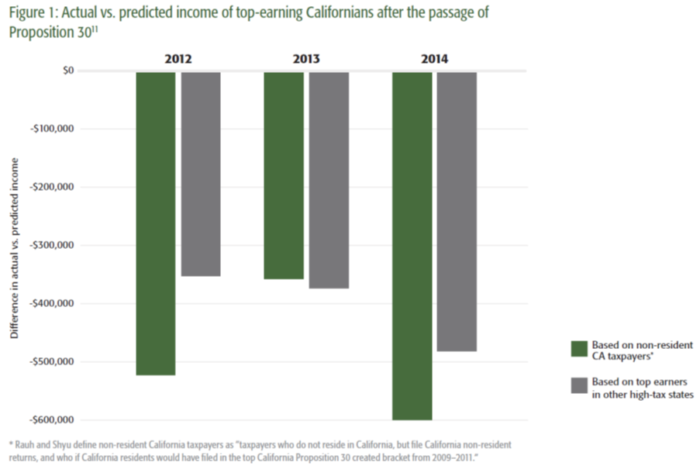
The new paper draws on a 2019 study from the National Bureau of Economic Research that examined behavior responses to Proposition 30, finding that such responses “eroded 60.9% of [new] tax revenues by [the law’s] second year.” This led the 2019 paper’s authors to speculate that California may be able to increase state tax revenues by reducing tax rates on certain high-income households, which may result in more incentive to generate income and less incentive to engage in tax avoidance activities. The authors also found that for those Californians earning over $5 million, the rate of departures spiked 42 percent, from 1.5 percent after the 2011 tax year to 2.125 percent after the 2012 tax year.
In other cases, higher income taxes directly affect pass-through businesses, which pay taxes through the individual returns of their owners, rather than through company returns. In California, sole proprietorships alone account for some $150 billion in economic activity every quarter, and this amount doesn’t include S corporations, partnerships, limited liability companies, and other forms of pass-through entities.
Many pass-through businesses have gone on to become large, successful corporations, such as Marriott, JCPenney, Walmart, Kinko’s, and eBay, the latter two of which were founded in California. But in a harsh tax and regulatory climate for businesses, in the words of Elon Musk, California “has a forest of redwoods and the little trees can’t grow.”
California’s state budget is heavily reliant on the wealthy. In 2019, 40 percent of individual income tax revenue came from filers with incomes over $1 million. Continuing to rely on revenue from such a narrow slice of the population for core services like education is unsustainable, likely increasing revenue volatility and necessitating harsh budget cuts during future recessions.
“A CEO who wants to leave California, where the nearest abutting state is a four-hour drive from a major economic center, has to hire all new people and put the company’s customer base at risk, and they are still leaving,” said Pioneer Institute Executive Director Jim Stergios. “For Massachusetts CEOs the calculus on moving is simpler. If we pass the graduated income tax, every other New England state will boast lower top income tax rates than Massachusetts. Even Connecticut, which has suffered job losses, an exodus of businesses, and tax revenue difficulties because of its own bad tax policies, will have a lower top rate than Massachusetts.”
About the Author
Andrew Mikula is Economic Research Analyst at Pioneer Institute. Mr. Mikula was previously a Lovett & Ruth Peters Economic Opportunity Fellow at Pioneer Institute and studied economics at Bates College.
About Pioneer
Pioneer’s mission is to develop and communicate dynamic ideas that advance prosperity and a vibrant civic life in Massachusetts and beyond.
Pioneer’s vision of success is a state and nation where our people can prosper and our society thrive because we enjoy world-class options in education, healthcare, transportation, and economic opportunity, and where our government is limited, accountable and transparent.
Pioneer values an America where our citizenry is well-educated and willing to test our beliefs based on facts and the free exchange of ideas, and committed to liberty, personal responsibility, and free enterprise.
Get Updates on Our Economic Opportunity Research
Related Posts: