New Study Finds Pandemic-Spurred Technologies Lowered Barriers to Exit in High-Cost States
Read coverage of this report in the Boston Herald, The Boston Globe, and State House News Service.
BOSTON – Both employers and households will find it easier to leave major job centers as technologies made commonplace by the COVID-19 pandemic have led to a rethinking of the geography of work, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute.
“The pandemic has changed the calculus on whether telecommuting is worth it, for both employers and workers,” said Andrew Mikula, author of “Barriers to Exit Lowered in High-Cost States as Pandemic-Related Technologies Changed Outlook.”
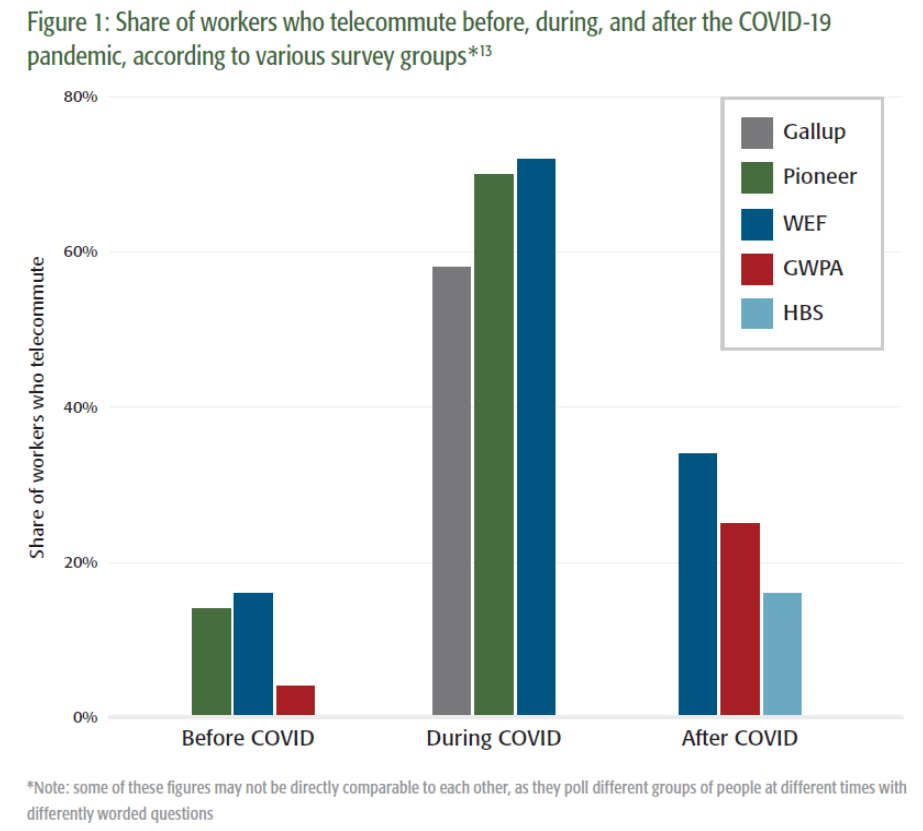
The study draws on survey data projecting that a third of workers could be permanent telecommuters by the end of 2021 and discusses implications of these trends for transportation, municipal finance, and wealth migration. While worst-case scenarios could bring a level of disinvestment in places like New York City not seen since the 1970s, even a mid-range scenario suggests a significant relocation of jobs and potentially wealth.
Before COVID-19, many high earners and large companies were already leaving New York and Silicon Valley. Coupled with the role of prominent vacation spots in providing a haven for those of means, more business- and tax-friendly areas like Florida, Texas, and Arizona are the clear winners of these trends. As demonstrated in a recent Pioneer study, “Do the Wealthy Migrate Away From High-Tax States?”, relocation of jobs and wealth from Massachusetts has been largely to Florida and New Hampshire.
“These trends are not new, but the pandemic has served as an accelerant,” said Pioneer Institute Executive Director Jim Stergios. “Policymakers who care about recovering the pandemic’s lost jobs will need to create a more business-friendly environment. That means a focus on policies related to taxes, regulation, and the additional costs we are imposing on small employers.”
Policymakers face risks on both sides of the employment equation. Both employees and employers see benefits from remote work. Polls show that a quarter of workers would be willing to take a 10-percent pay cut for the opportunity to work remotely, perhaps a small price to pay to be able to escape the exorbitant cost of living in Boston or New York. Research shows that remote work also reduces the direct costs associated with working in an office environment, such as parking, food, and travel for employees, by an average of $4,000 annually.
For employers, savings average $11,000 per worker, largely because of productivity gains and less need for real estate.
Some argue that the attraction of urban amenities and the productivity advantage of large cities will outweigh the added expenses and short-term public health concerns. Still, surveys suggest that a sizable segment of business executives, office workers, and other professionals will choose to operate remotely for the foreseeable future.
The response from policymakers will be telling and likely determine a set of winners and losers in the new post-pandemic economic reality. Some policymakers will double down on the burdensome tax and regulatory environments that started the taxpayer exodus in the first place; others will take action to offset the obvious financial and quality-of-life benefits of remote work. Based on the policy path taken, employers and employees will make their own decisions about job location and investments.
About the Author
Andrew Mikula is a Research Assistant at Pioneer Institute. Mr. Mikula was previously a Lovett & Ruth Peters Economic Opportunity Fellow at Pioneer Institute and studied economics at Bates College.
About Pioneer
Pioneer’s mission is to develop and communicate dynamic ideas that advance prosperity and a vibrant civic life in Massachusetts and beyond.
Pioneer’s vision of success is a state and nation where our people can prosper and our society thrive because we enjoy world-class options in education, healthcare, transportation, and economic opportunity, and where our government is limited, accountable and transparent.
Pioneer values an America where our citizenry is well-educated and willing to test our beliefs based on facts and the free exchange of ideas, and committed to liberty, personal responsibility, and free enterprise.
Get Updates on Our Economic Opportunity Research
Related Research