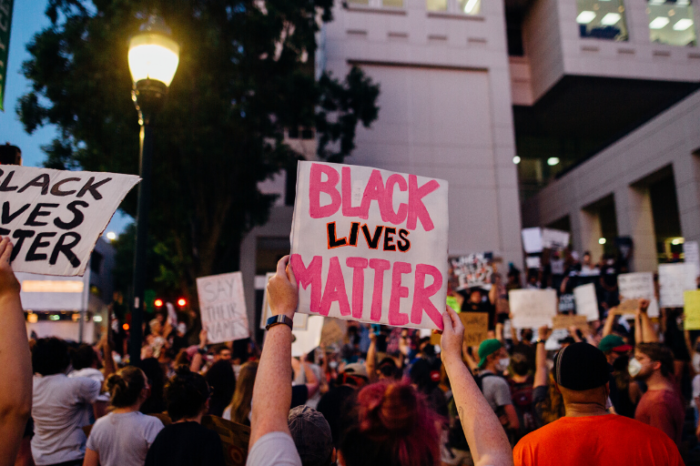Sensible police reform includes changing ‘qualified immunity’ laws
This op-ed originally appeared in WGBH News, The Lowell Sun, The Fitchburg Sentinel & Gazette, Salem News, and the Gloucester Daily Times.
By Jim Stergios and Charlie Chieppo
Even in a time of painful divisions in our country, there is little doubt among people of good faith that what Derek Chauvin and three other former Minneapolis police officers did to George Floyd was criminal. If they are indeed convicted of a felony, how is it that the former officers could very well be immune from civil liability?
The answer lies in Harlow vs. Fitzgerald, a 1982 U.S. Supreme Court case. There, the justices ruled that public officials should have “qualified immunity.” In practice, qualified immunity nearly exempts public officials from civil liability for their actions, no matter how egregious. The Court found that officials can only be found liable if they violate “clearly established law.” As applied to the Floyd case, it means that unless there is a federal case finding that kneeling on a person’s neck until the person dies is illegal, Chauvin wouldn’t incur civil liability.
If you think that couldn’t possibly be true, consider the Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals’ 2019 decision in Baxter vs. Bracey. A panel of judges found that two police officers who unleashed a dog on a suspect who was sitting down with his hands up were entitled to qualified immunity because, even though an earlier ruling found that officers were not allowed to sic a dog on someone who was lying down, no case ever addressed whether the same was true for a suspect who was sitting with his hands up.
For Americans to have faith in our legal system, the system must be rational, and providing felons with immunity from civil liability doesn’t pass the smell test. Nor does the idea that public officials can violate our rights with impunity as long as they come up with a way to do it that no federal court has yet addressed.
In the wake of Floyd being killed, a bill introduced by Rep. Justin Amash of Michigan would bring us closer to the ideals outlined in the Constitution. Massachusetts Rep. Ayanna Pressley is among more than 50 co-sponsors of the “Ending Qualified Immunity Act.”
The need for such legislation was highlighted just this month, when the Supreme Court refused to hear several cases that challenge qualified immunity, including Baxter vs. Bracey.
Freedom from bad faith violations of our constitutional rights by those sworn to uphold them is among the most basic things we expect from government. We cannot have a healthy republic if public officials don’t respect our rights, and subjecting public officials who trample individual liberties to civil liability is the surest way to protect those rights.
Ending qualified immunity from civil liability would help restore faith in our system, ensure respect for constitutional rights and provide a fair remedy to George Floyd, his family and other victims of bad faith violations. Let’s use this moment of near unanimity about the horror of what was done to Floyd to prevent others from having their rights trampled by the very people we rely on to protect them.
Get Our COVID-19 News, Tips & Resources!
Browse our recent commentary: