New Study Provides Toolkit for Crafting Education Tax-Credit Scholarship Programs
Comes on the heels of U.S. Supreme Court striking down “Anti-Aid” or “Blaine” Amendments to Massachusetts and other state constitutions that prohibited use of public funds for private schools
Media coverage of the report in The 74: With DeVos Out, Movement for Private School Choice Shifts to State Legislatures
BOSTON – In the wake of a U.S. Supreme Court ruling that struck down a key impediment to private school choice, Pioneer Institute has published a toolkit for designing tax-credit scholarship (TCS) programs.
Under these programs, individual and corporate taxpayers receive tax credits for contributions to scholarship granting organizations (SGOs) that fund students attending schools other than their assigned district school. The SGOs are non-profits registered under the state TCS program.
Get Updates on Our School Choice Research
“Policymakers should craft TCS programs to maximize the incentives for taxpayers to contribute to SGOs, the number of families that can benefit from the scholarships and the freedom and flexibility SGOs have to serve those families,” said Jason Bedrick, author of “Earning Full Credit: A Toolkit for Designing Tax-Credit Scholarship Policies.”
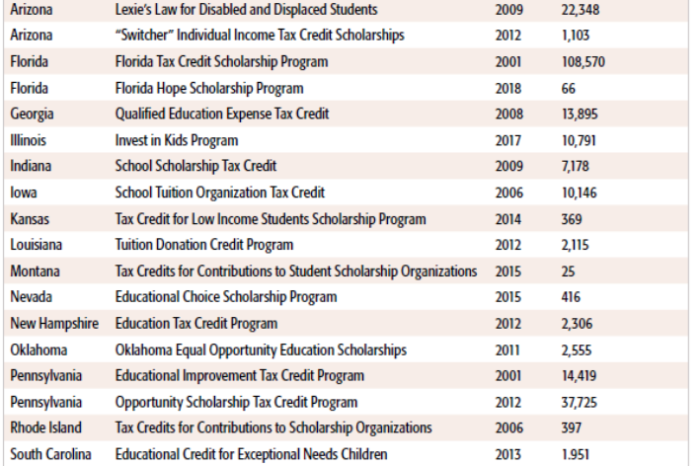
Tax-credit scholarships are the most common private-school choice program. There are currently 23 programs in 18 states and Utah enacted a 24th program earlier this year.
Number of tax-credit scholarships granted by state
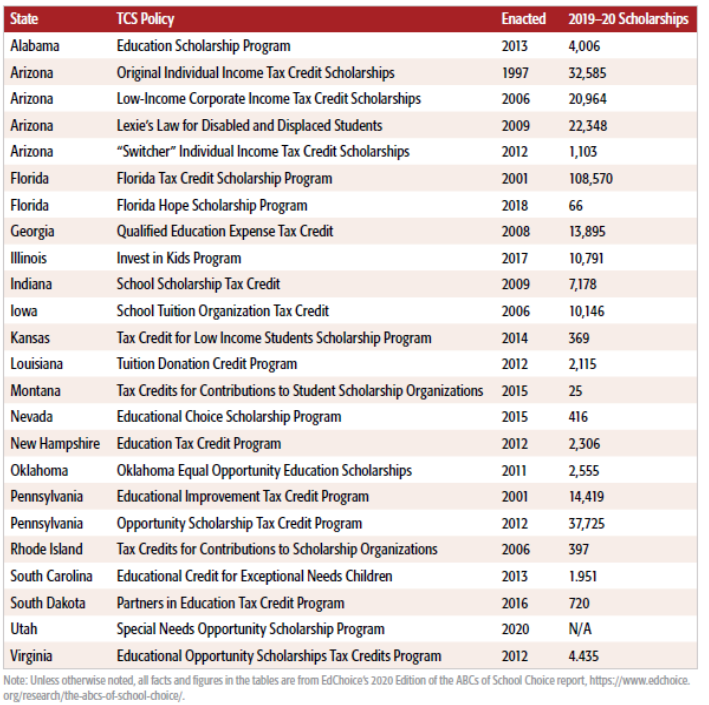
The programs are popular among parents and taxpayers. In a 2018 survey of more than 14,000 scholarship families in Florida, 92 percent expressed satisfaction with the program and about 90 percent were satisfied with the school their child attended using a scholarship. According to the 2020 Education Next survey, 57 percent of Americans support TCS policies. Support is even higher among parents (61 percent) and Americans who are Black (68 percent) and Hispanic (70 percent). According to EdChoice’s 2020 “Schooling in America” survey, 69 percent of the general public supported TCS policies.
Programs can be revenue neutral or even produce savings for the state if the value of tax credits is less than the money saved in school districts that no longer educate students taking advantage of tax-credit scholarships.
Bedrick makes a number of recommendations for policymakers crafting TCS programs. He urges states to make all children eligible for the scholarships but to prioritize those who are most in need. Around two thirds of current programs impose income-based eligibility restrictions.
Tax credits should be as close to 100 percent as possible to encourage taxpayers to contribute. Credits currently range from 50 to 100 percent. Just over half the programs offer a 100 percent credit and around another 30 percent offer 75 to 90 percent credits.
Policymakers should aim to cap credits at a level that is sufficient to provide scholarships to all families who want one. Limits should include “escalator clauses” that automatically raise caps over time to keep up with demand. In Florida, for example, every time families claim at least 90 percent of the credits, the credit cap is increased by 25 percent the following year.
The scholarships themselves should be as close as possible to the state portion of per-pupil spending in K-12 public schools and should be eligible to be used for related expenses such as tutoring, online courses and educational therapy.
States should respect the ability of SGOs to set their own mission. Some provide scholarships for students to attend religious schools, others focus on a particular pedagogical approach such as Montessori schools, while still others focus on a geographical area.
In terms of accountability, Bedrick urges policymakers not to require scholarship students to take a specified standardized test. Instead, schools should be able to choose from among many norm-referenced tests. This would give parents information about their children’s progress without unduly restricting how schools operate.
The study includes a foreword by Kendra Espinoza, who was the lead plaintiff in Espinoza v. Montana Department of Revenue, the case in which the Supreme Court struck down so-called Blaine or Anti-Aid Amendments, such as one in Massachusetts, that prohibited public money from flowing to private schools. “Earning Full Credit” also features an introduction from noted education reform expert Theodor Rebarber.
About the Authors
Jason Bedrick is director of policy for EdChoice. Previously, Bedrick served as policy analyst with the Cato Institute’s Center for Educational Freedom. He also served as a legislator in the New Hampshire House of Representatives and was an education policy research fellow at the Josiah Bartlett Center for Public Policy. Bedrick received his master’s degree in public policy from the John F. Kennedy School of Government at Harvard University, where he was a fellow at the Taubman Center for State and Local Government.
Kendra Espinoza is the lead plaintiff in the landmark U.S. Supreme Court case, Espinoza v. Montana Department of Revenue. She is a working, single mother of daughters Naomi and Sarah, who attend Stillwater Christian School. They were recipients of Montana’s education tax credit program until the Montana Department of Revenue, citing the state’s Blaine Amendment, issued a rule excluding Stillwater Christian from the program on religious grounds.
Theodor Rebarber has worked on education reform and policy for three decades in the public, nonprofit and private sectors. He is currently CEO of nonprofit AAT (aateducation.org), which recently received a grant from the National Endowment for the Humanities (NEH) to develop an American History curriculum for high school. The curriculum will be based on historian Wilfred McClay’s outstanding new textbook Land of Hope. Rebarber’s other recent work has included: analysis of the impact of Common Core on student achievement; review of state mandates in school choice programs, and; development of an online testing platform serving 40,000 students, and; management of a consortium of five states that developed a large-scale standardized assessment. He was co-founder and chief education officer of a charter school company that accelerated academic achievement for 10,000, primarily disadvantaged students across 10 states. Rebarber served as senior staff in Congress, where he was the lead staff author of the federal charter schools statute for Washington, D.C., as well as legislation to improve traditional public schools and offer school choice to disadvantaged families. He worked at the U.S. Education Department’s office of research as well as serving as a research associate at the Vanderbilt Institute for Public Policy Studies (VIPPS). He has testified before Congress and state legislatures as well as developed a range of education policy analyses and publications, including on state and national curriculum standards and assessments, school choice, education costs, accountability systems, differential and performance- based teacher compensation, program evaluation and teacher certification.
About Pioneer
Pioneer’s mission is to develop and communicate dynamic ideas that advance prosperity and a vibrant civic life in Massachusetts and beyond.
Pioneer’s vision of success is a state and nation where our people can prosper and our society thrive because we enjoy world-class options in education, healthcare, transportation and economic opportunity, and where our government is limited, accountable and transparent.
Pioneer values an America where our citizenry is well-educated and willing to test our beliefs based on facts and the free exchange of ideas, and committed to liberty, personal responsibility, and free enterprise.
Related Posts