How would a tax increase impact the MA economy?
/in Blog: Economy, Economic Opportunity, Featured /by Editorial Staff Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on
LinkedIn
+
Pioneer’s Charlie Chieppo explains how an income tax hike in Massachusetts will impact retirees and small business owners – not just the “super rich.”
Get Updates on Our Economic Opportunity Research
Additional Pioneer reports on the Mass. economy:
Related Posts
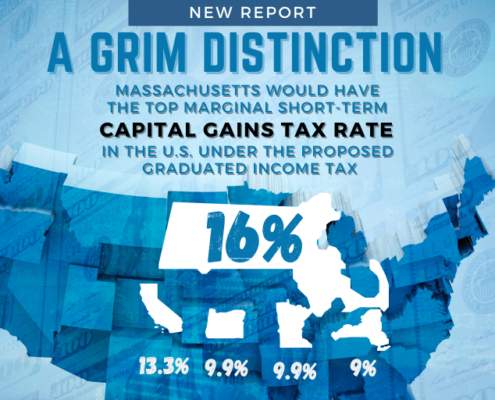
Study Warns Massachusetts Tax Proposal Would Deter Investment, Stifling the “Innovation Economy”
A state constitutional amendment promoted by the Massachusetts Teachers Association and the Service Employees International Union adding a 4 percent surtax to all annual income above $1 million could devastate innovative startups dependent on Boston’s financial services industry for funding, ultimately hampering the region’s recovery from the COVID-19 economic recession, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute.

Study Shows the Adverse Effects of Graduated Income Tax Proposal on Small Businesses
The state constitutional amendment promoted by the Massachusetts Teachers Association and the Service Employees International Union to add a 4 percent surtax to all annual income above $1 million will adversely impact a significant number of pass-through businesses, ultimately slowing the Commonwealth’s economic recovery from COVID-19, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute.

Study: Graduated Income Tax Proposal Fails to Protect Taxpayers from Bracket Creep
The state constitutional amendment proposed by the Service Employees International Union and the Massachusetts Teachers Association to add a 4 percent surtax to all annual income above $1 million purports to use cost-of-living-based bracket adjustments as a safeguard that will ensure only millionaires will pay. But historic income growth trends suggest that bracket creep will cause many non-millionaires to be subject to the surtax over time, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute.

Pioneer Institute, The Immigrant Learning Center Co-Produce New Weekly Podcast
Pioneer Institute is pleased to announce the launch of JobMakers, a new weekly podcast that explores the world of risk-taking immigrants who create new products, services, and jobs in New England and across the United States. JobMakers is produced in collaboration with The Immigrant Learning Center (ILC) of Malden, MA.

New Study Warns Graduated Income Tax Will Harm Many Massachusetts Retirees
If passed, a constitutional amendment to impose a graduated income tax would raid the retirement plans of Massachusetts residents by pushing their owners into higher tax brackets on the sales of homes and businesses, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute. The study, entitled “The Graduated Income Tax Trap: A retirement tax on small business owners,” aims to help the public fully understand the impact of the proposed new tax.

Study: Graduated Income Tax Proponents Rely on Analyses That Exclude the Vast Majority Of “Millionaires” to Argue Their Case
Advocates for a state constitutional amendment that would apply a 4 percent surtax to households with annual earnings of more than $1 million rely heavily on the assumption that these proposed taxes will have little impact on the mobility of high earners. They cite analyses by Cornell University Associate Professor Cristobal Young, which exclude the vast majority of millionaires, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute.

Report Contrasts State Government and Private Sector Employment Changes During Pandemic
Massachusetts state government employment has been virtually flat during COVID-19 even as employment in the state’s private sector workforce remains nearly 10 percent below pre-pandemic levels, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute. The study, “Public vs. Private Employment in Massachusetts: A Tale of Two Pandemics,” questions whether it makes sense to shield public agencies from last year’s recession at the expense of taxpayers.

A wealth tax, a SCOTUS case, and a likely Mass. exodus
Op-ed in The Boston Globe: A case New Hampshire filed with the US Supreme Court last October against the Commonwealth of Massachusetts could have a huge impact on state finances nationwide. It also raises the stakes as the Massachusetts Legislature considers amending the state constitution to eliminate the state’s prohibition against a graduated income tax and to hike taxes on high earners.

Study Finds Massachusetts Graduated Income Tax May Be a “Blank Check” and Not Increase Funding for Designated Priorities
Advocates claim a proposed 4 percent surtax on high earners will raise nearly $2 billion per year for education and transportation, but similar tax hikes in other states resulted in highly discretionary rather than targeted spending, according to a new policy brief published by Pioneer Institute. That same result or worse is possible in Massachusetts because during the 2019 constitutional convention state legislators rejected — not just one, but two — proposed amendments requiring that the new revenues be directed to these purposes.

Enacting ‘Millionaires’ Taxes’ Will Set Back State Recoveries
Even as countless citizens and businesses are struggling, many state governments are faced with large deficits that hinder their ability to help. As a result, some, such as Massachusetts, are considering raising taxes on high-earners to generate revenue. But in its report, “Connecticut’s Dangerous Game: How the Nation’s Wealthiest State Scared Off Businesses and Worsened Its Financial Crisis,” the Boston-based Pioneer Institute provides a cautionary tale about the dangers of going down the path taken by the Bay State’s neighbor, Connecticut.

Report: Proposed Graduated Income Tax Might Not Increase State Education and Transportation Spending
While supporters of a state constitutional amendment that would impose a 4 percent tax rate hike on annual income over $1 million claim additional revenue from the surtax will fund public education and transportation needs, the amendment in no way assures that there will be new spending on these priorities. In fact, without violating the amendment, total state education and transportation funding could stay the same or even fall, according to a new review published by Pioneer Institute.
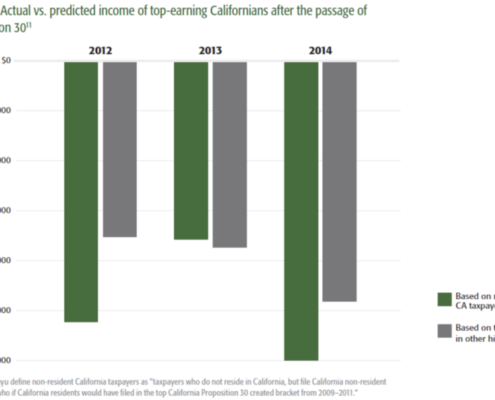
New Study Highlights Economic Fallout from California’s 2012 Tax Hike
A 2012 income and sales tax increase in California, named “Proposition 30,” stifled business activity, accelerated out-migration among the wealthy, and ultimately reduced the state’s tax base, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute that aims to share empirical data about the impact of tax policy decisions.



