Is Boston’s Health Care Industry Still Growing? Here’s What the Data Says.
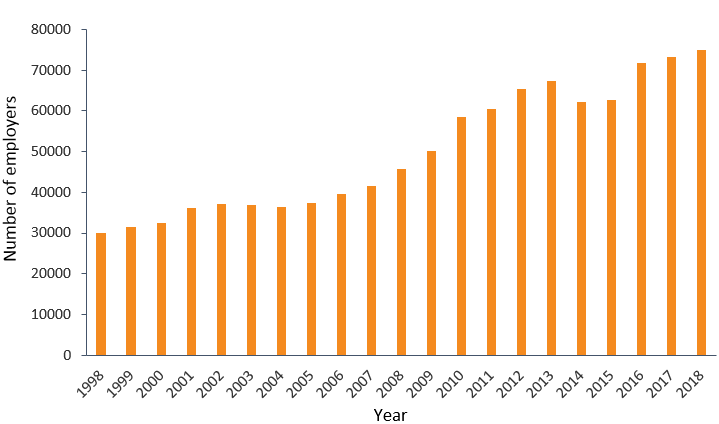
From 1998 to 2018 in Massachusetts, employment in the Health Care and Social Assistance sector grew by 45% and the number of establishments grew by 149%, as seen in Figures 1.a. and 1.b. below. The number of establishments has increased steadily over time with the exception of 2014-2015, while employment growth has fluctuated after the 2008 recession. Generally, year-to-year changes in employment and the number of establishments are positively correlated, with the major exception of the recession in 2008-2010, in which employment in the industry contracted and the number of business establishments grew.
Figure 1.a. The number of employees in the Health Care and Social Assistance industry in Massachusetts over time
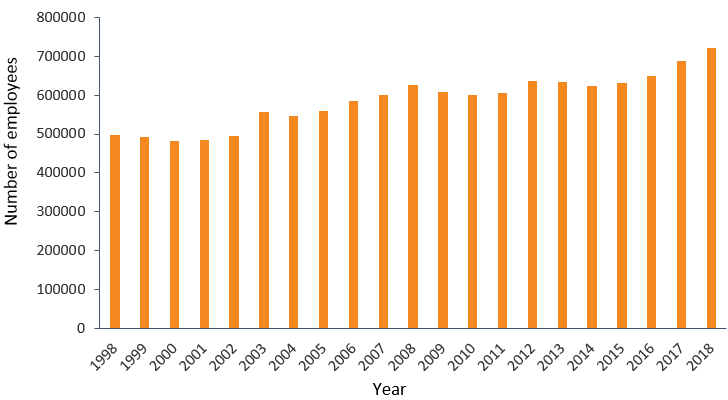
Figure 1.b. The number of employers in the Health Care and Social Assistance industry in Massachusetts over time
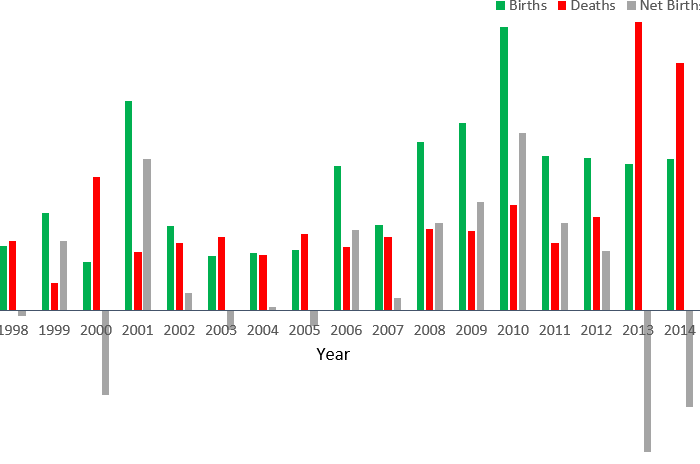
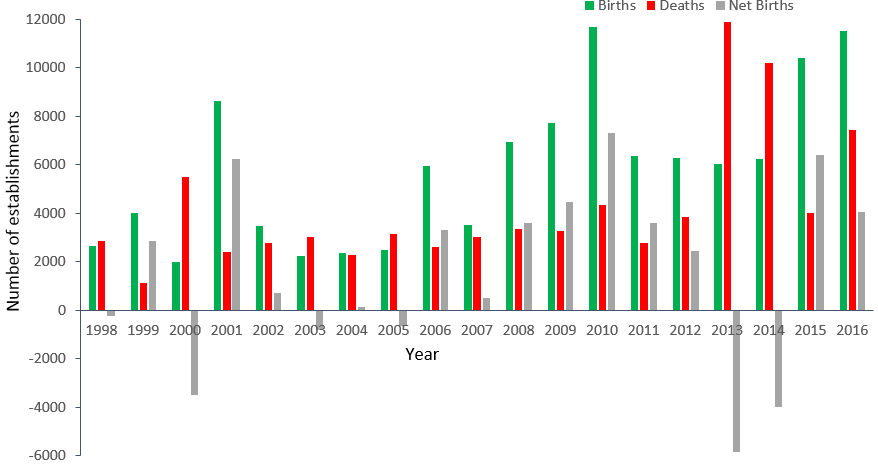
Between 1998 and 2016, there were 38% more business births than business deaths in the Health Care and Social Assistance industry in Massachusetts (see Figure 2 below). Generally, the level of business turnover has remained a stable percentage of total industry establishments over this period, but the absolute number of firms entering or exiting the market has increased as the industry has grown.
While the number of establishments in this industry generally increased between 1998 and 2016, the industry had a large number of establishments go out of business in 2013 and 2014. This is especially true in Suffolk and Worcester Counties, and the struggles of health care businesses in these areas in 2013 and 2014 may be related to a mini-boom in suburban development as the nation recovered from the 2008 housing crisis. In fact, Nantucket and Dukes Counties saw the largest gains in health care establishments between 2013 and 2018. In 2018, the number of health care establishments in Suffolk County (which includes Boston) remained 10% less than its 2013 peak.
Curiously, the number of new businesses in the Health Care and Social Assistance sector was higher during the Great Recession than in the prior period of economic expansion. This may be attributable to a significant growth in social and health care services targeted at financially struggling families and individuals. In fact, there is another spike in business births in this industry in 2001, also a recession year. A smaller surge in the number of industry births in 2006 notably coincides with a state-level health care reform under Chapter 58 enacted in that year.
The number of business deaths is very stable until 2013. The net business births figure for the industry has proved quite volatile in recent years, with a couple annual swings of over 5,000 net births.
Figure 2: The number of business births and deaths in the Health Care and Social Assistance industry in Massachusetts over time
More information on business trends, whether by industry, geography, or in the aggregate, is available at MassEconomix.com.
Andrew Mikula is the Lovett & Ruth Peters Economic Opportunity Fellow at the Pioneer Institute. Research areas of particular interest to Mr. Mikula include urban issues, affordability, and regulatory structures. Mr. Mikula was previously a Roger Perry Government Transparency Intern at the Institute and studied economics at Bates College.
Get Updates on Our Economic Opportunity Research