New Study Finds Tax Policy Drives Connecticut’s Ongoing Fiscal & Economic Crisis
BOSTON – Multiple rounds of tax increases aimed at high earners and corporations triggered an exodus from Connecticut of large employers and wealthy individuals, according to a new study published by Pioneer Institute.
“It’s no coincidence that the state’s ongoing economic struggles have corresponded with a string of experimental tax hikes,” said Greg Sullivan, who co-authored “Connecticut’s Dangerous Game: How the Nation’s Wealthiest State Scared Off Businesses and Worsened Its Fiscal Crisis,” with Andrew Mikula.
Over the last quarter-century, Connecticut has endured a series of budget crises. To cover ballooning costs, the state enacted sharp tax increases, including four income tax hikes in the last 20 years that caused the top rate to jump by 77 percent.
Connecticut Governor Ned Lamont said that the tax increases “totally disadvantage the state,” noting that it already has “some of the highest income tax rates in the country and we pay a price for that.”
In recent years, Connecticut has increasingly turned to high earners and large companies to close budget gaps, doubling a surcharge on large firms, establishing and then increasing a tax on luxury goods, and raising the income tax for the state’s highest earners.
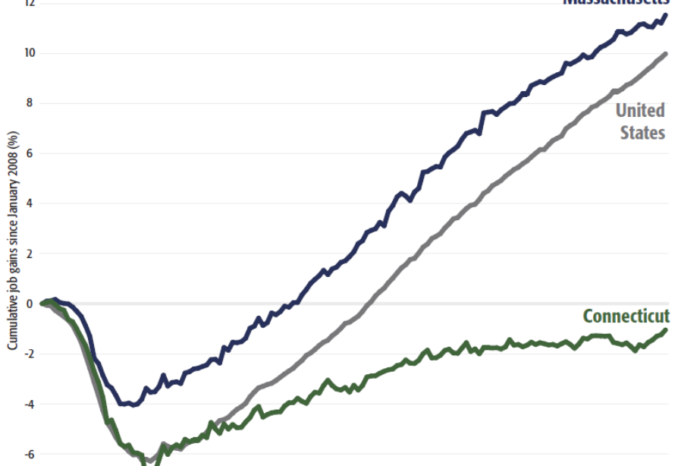
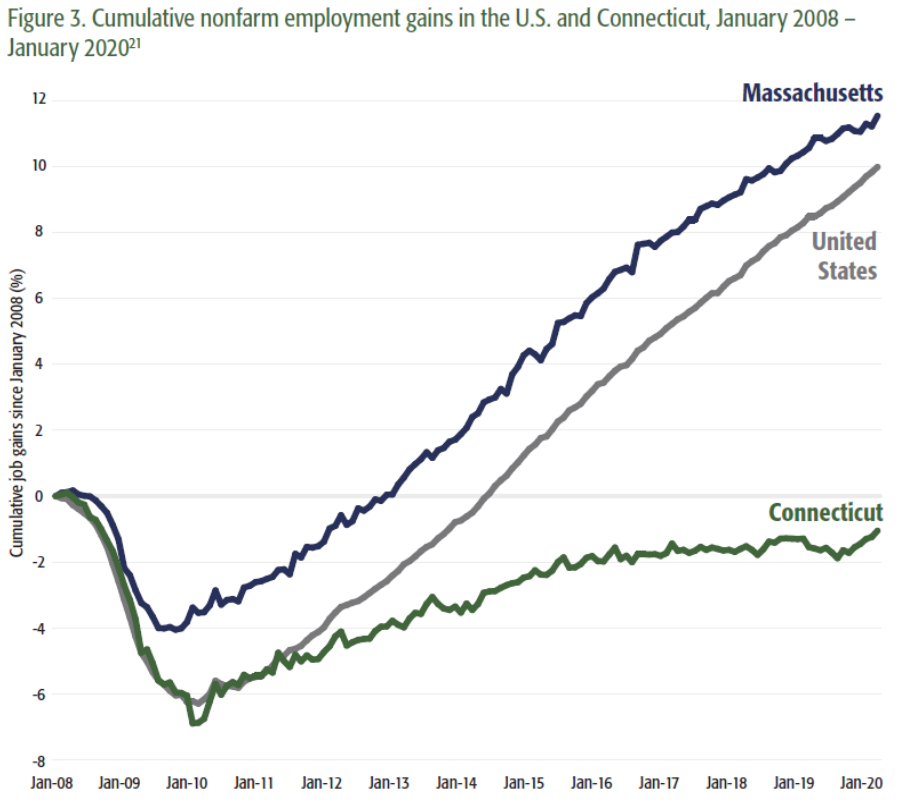
The results have been disastrous. From 2008 to 2020, the state placed 49th among the states in private sector wage growth. In just the last couple of years, General Electric and Alexion Pharmaceuticals both moved their headquarters to Massachusetts. The flight of jobs has in turn affected existing homeowners, and before COVID-19, property values in wealthy Fairfield County were still 18 percent below their 2006 peak.
Further, these tax increases have failed to stabilize Connecticut’s finances, and large deficits continue to be projected for the state.
According to 2016 Connecticut Department of Revenue Services data, the state’s wealthiest 3 percent of families account for 41 percent of all income tax revenue. Between 2012 and 2018, Connecticut lost high earners at a rate that trailed only Washington, D.C., and those who fled earned more on average than taxpayers who migrated into the state.
Despite rate increases, the amount of taxes paid by Connecticut’s 100 top taxpayers plummeted 45 percent between 2015 and 2016 alone.
Massachusetts took a very different approach in the wake of the 1990-91 recession. A state income tax that was once 6.25 percent now stands at 5.0 percent. In recent years, the Commonwealth has gained millionaires at a higher rate than the national average, and nearly twice the rate of Connecticut.
Between January 2008 and January 2020, employment in Massachusetts grew by 12.5 percent. In contrast, Connecticut still hasn’t recovered all the jobs it lost during the Great Recession, and those it has created are, on average, lower paying.
Massachusetts has also benefited from Connecticut’s struggles to retain major corporations and wealthy individuals, and Connecticut is one of the few states from which taxable income migration to Massachusetts has been positive in recent years. That said, wealth migration remains a concern in Massachusetts, especially given the large scale of tax avoidance.
“Leaving has never been easier,” said Pioneer Institute Executive Director Jim Stergios. “In some cases, high earners can stay put and simply move money into trusts located in other states.”
About the Authors
Andrew Mikula is a Research Assistant at Pioneer Institute. Mr. Mikula was previously a Lovett & Ruth Peters Economic Opportunity Fellow at Pioneer Institute and studied economics at Bates College.
Gregory Sullivan is Pioneer’s Research Director. Prior to joining Pioneer, Sullivan served two five-year terms as Inspector General of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts and was a 17-year member of the Massachusetts House of Representatives. Greg is a Certified Fraud Investigator, and holds degrees from Harvard College, The Kennedy School of Public Administration, and the Sloan School at MIT.
Pioneer’s mission is to develop and communicate dynamic ideas that advance prosperity and a vibrant civic life in Massachusetts and beyond.
Pioneer’s vision of success is a state and nation where our people can prosper and our society thrive because we enjoy world-class options in education, healthcare, transportation, and economic opportunity, and where our government is limited, accountable and transparent.
Pioneer values an America where our citizenry is well-educated and willing to test our beliefs based on facts and the free exchange of ideas, and committed to liberty, personal responsibility, and free enterprise.
Get Updates on Our Economic Opportunity Research
Related Posts